
Things You Need After Knee Replacement Surgery. This is a rare but known complication following knee replacement surgery.
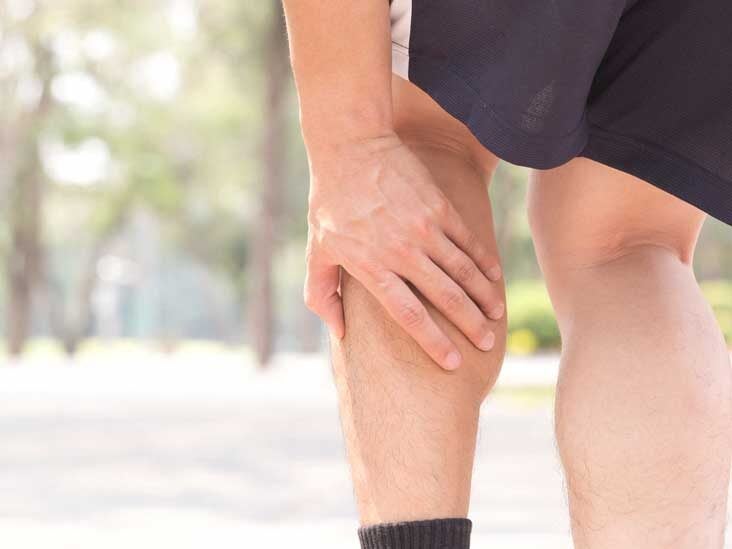
Increased pain in the calf or tenderness surrounding the knee.
Calf pain after knee surgery. Calf pain after knee replacement can happen for many reasons but after surgery the most common reason is weakness swelling and change in activity levels. These exercises will help improve calf mobility increase strength and condition the calf to handle the workload associated with normal walking. I had my second knee surgery two weeks ago and the day after surgery the pain in my calf started.
My calf looks bruised and slightly swollen and very tight. My knee is 95 better but my calf is killing me. I can warm it up and walk normally for an hour or two but if I stop even for a few minutes it stiffens up.
Calf pain is not normal after knee surgery. I would go back to your orthopedic surgeon as soon as possible. You can possible have a blood clot in your.
Abnormal Postsurgical Pain. These factors are signs you may have a complication. Increased pain in the calf or tenderness surrounding the knee.
This could be a warning sign of a blood clot in your leg. Notify your physician immediately if you suspect a blood clot. Sudden onset of chest pain.
Chest pain accompanied by shortness of breath may be a sign of pulmonary embolism. This occurs when a blood clot. Pain after a knee replacement in the knee region could be due to aseptic loosening of the prosthesis.
The calf swelling and pain could be due to a deep. This is a rare but known complication following knee replacement surgery. The typical pain from nerve pain is burning with numbness itchiness or tingling.
You may also have caused damage at the surgery site. You are supposed to use crutches for 10-15 days or until normal gait is attained by physiotherapy and rehab program. Pain in the calf area can also be due to pinched spinal nerves in the lumbo-sacral area or a pinched nerve at the knee joint.
A nerve conduction study should be done. Claudication pain in the calf is usually described as cramping and results from narrowing of the artery in the mid-thigh superficial femoral or the knee popliteal artery. Fracture of Lower Leg Bone.
Knee replacement pain after three months Swelling and bruising can continue for three months or more following knee replacement surgery. However it varies from patient to patient and depends on the condition you were in before surgery. Many patients are back to their activities without the pain they had before surgery by this stage of recovery.
The hallmark of this is pain that is gone initially after surgery but then spontaneously returns. Postoperative inflammation of the nerve root can mimic a recurrent disc–with a return of pain 2-7 days after surgery–but will usually subside with time and rehabilitation. See Microdiscectomy Microdecompression Spine Surgery.
Things You Need After Knee Replacement Surgery. Afterward I go in the hot tub for 5 to 10 minutes and work on my range of motion before taking a shower and walking a mile home. On alternating days I swim a half-mile ride a bicycle 6 miles or take a 3-mile walk.
Although I was in pain and limping before surgery I was always active. General pain may occur for up to several weeks following a total knee replacement. Swelling typically lasts for 2 to 3 weeks after surgery but may persist for as long as 3 to 6 months.
26 years experience Orthopedic Surgery. Although calf pain can occur after knee arthroscopy the concern is the potential for a deep venous thrombosis otherwise known as a blood clot. The biggest symptoms of nerve damage after surgery are usually numbness tingling burning or muscle weakness or atrophy.
Many times nerve issues after surgery are temporary for example many patients have nerve problems after surgery that. The AAOS state that most people can start doing some normal daily activities 36 weeks after surgery and start driving 46 weeks after surgery. Calf muscle pain is a common problem that can make walking running and jumping difficult and painful.
Pain in the calf region may be due to an injury such as a calf muscle strain an underlying medical condition or a problem in the nerves or arteries in the lower leg.