Chest pain is only one of the possible signs of an impending heart attack. Do not try to ignore chest pain and work or play through it Chest pain is.
Chest pain is one of the main symptoms of costochondritis.
What does chest pain mean. Chest pain and heart attack symptoms. Chest pain is only one of the possible signs of an impending heart attack. If you notice one or more of the signs below in yourself or someone else call 911 or your local emergency number right away.
Uncomfortable pressure squeezing fullness burning tightness or pain in the center of the chest. While chest pain is a well-established sign of a heart attack it can also be caused by many other less serious conditions. About 13 percent of all emergency room ER visits for chest pain result.
Atypical chest pain refers to chest pain that is not typical of the kind caused by a heart attack. The definition of atypical chest pain is not clear and different people may mean different things by atypical chest pain. Many things can cause atypical chest pain and a few are described below.
This is sometimes described as a stabbing pain or a feeling of tightness pressure or squeezing. This is sometimes described as feeling like a. Chest pain is one of the main symptoms of costochondritis.
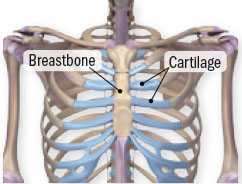
This condition happens when your rib cage cartilage becomes inflamed. Chest pain or discomfort is a common symptom of a heart attack in both men and women. Anyone who experiences chest pain or discomfort that lasts for.
Chest pain can be a symptom of many different things ranging in severity from anxiety to pulling a muscle in the area to struggling with a lung or heart condition. Chest pain can also be due to a heart attack coronary occlusion aortic aneurysm dissection myocarditis esophageal spasm esophagitis rib injury or disease anxiety and other important diseases. Do not try to ignore chest pain and work or play through it Chest pain is.
What Does Chest Pain Mean. Chest muscle pain is rather common for a number of reasons and although the sensation can be somewhat alarming more often than not it is due to non-life-threatening issues. Common causes include increased activity with exercise an injury to the chest pneumonia or blood clot or violent coughing.